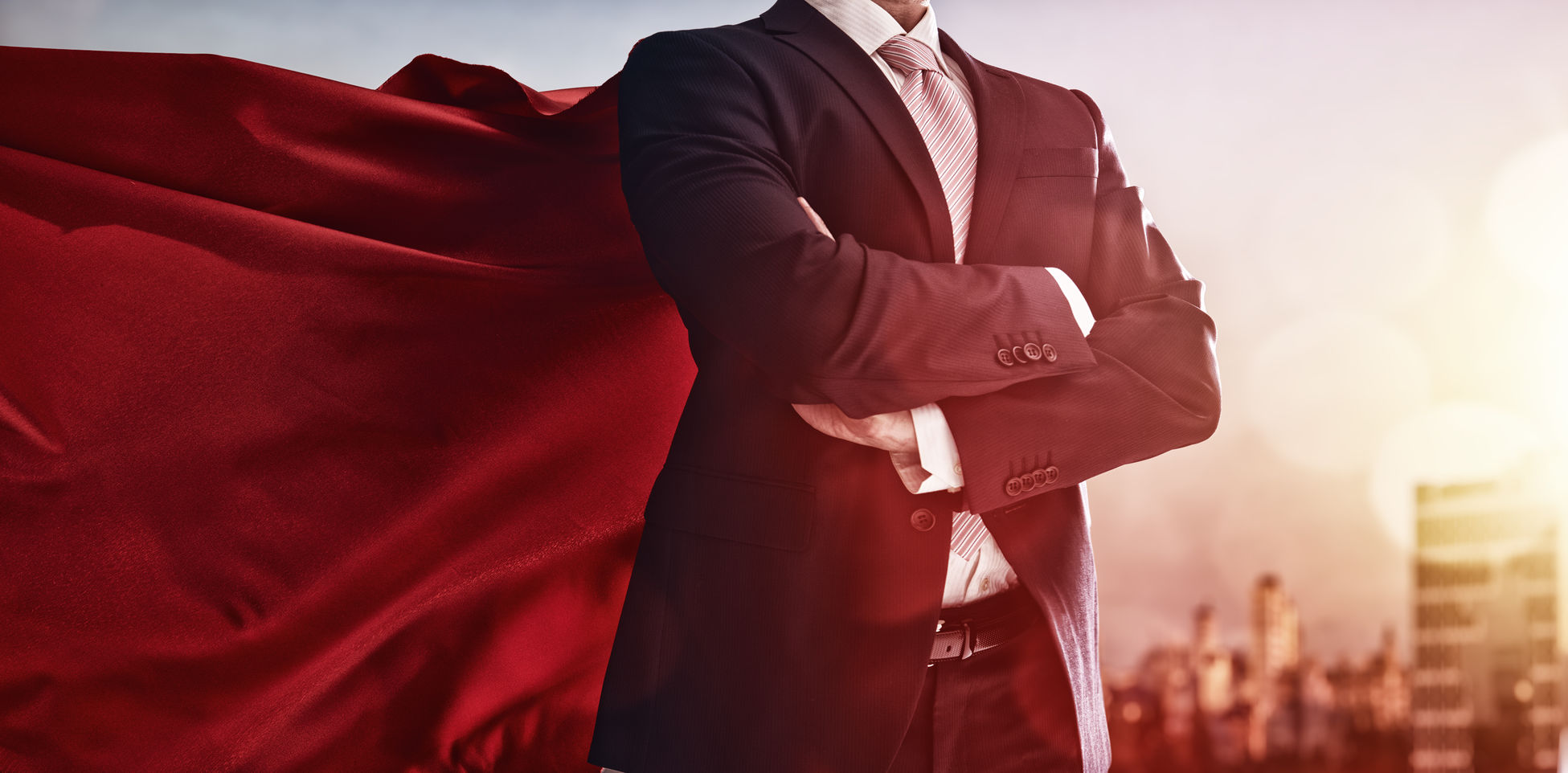
U jezičnom smislu, moć i vlast su dva sasvim različita pojma. No, s obzirom da se na engleskom jeziku ova dva pojma ponekad preklapaju u prijevodu, potrudit ćemo se pojasniti bitne razlike među njima.
Osnovna razlika između moći i vlasti je stupanj kontrole i utjecaja koji ovi pojmovi nude njihovom ‘korisniku’.
In linguistic terms, power and authority are two very distinct notions. Nevertheless, since the two notions occasionally overlap in translation, we will attempt to clarify the main differences between them
The main difference between power and authority is the degree of control and influence they offer to the possessor.
POWER – Max Weber, German sociologist and political economist defined power as the ability to achieve desired ends despite resistance from others. Power is the personal ability to control or influence others.
Example: “Democracies do not tolerate a display of power as it does not have the authority (legitimacy) of the people who elected it.”
MOĆ– Max Weber, njemački sociolog i politički ekonomist, definirao je moć kao sposobnost postizanja željenog cilja usprkos protivljenju drugih. Moć je osobna sposobnost kontroliranja ili utjecanja na druge ljude.
Primjer: „Demokratski ustrojene države ne toleriraju upotrebu moći jer joj nedostaje ovlast (legitimitet) koju daju ljudi/narod koji su je birali.
AUTHORITY (legitimate POWER) is the legal and legitimate ability to exercise power. It is the formal right to take decisions or make commands.
Example: “Vlada Republike Hrvatske predstavlja izvršnu vlast odnosno dužna je provoditi volju naroda koji joj je za to dao ovlast.”
VLAST je legalna i legitimna sposobnost upotrebe moći. Vlast je formalno pravo na donošenje odluka ili zapovijedi.
Primjer: „The Government of the Republic of Crotia represents the executive power i.e. it is obliged to exercise the will of the people who gave it the authority for that.“
Curiosity:
SEPARATION OF POWERS – is the principle that limits the powers vested in any person or institution. It divides governmental authority into legislative, executive and judiciary.
Example: “The Government of the Republic of Croatia exercises executive power in conformity with the Constitution and law.”
Zanimljivost:
TRODIOBA VLASTI – je načelo koje ograničava ovlasti dane osobi ili instituciji. Ustrojava vlast na zakonodavnu, izvršnu i sudbenu.
Primjer: „Vlada Republike Hrvatske obavlja izvršnu vlast u skladu s Ustavom i zakonima.“
Sources: Max Weber; Business Dictionary